Education

If you have any concerns about purchasing a diamond, our diamond education is the most thorough resource available. To help you make an informed diamond purchasing choice and get the most out of your diamond in terms of both look and value, we go beyond discussing the traditional “4 C’s” of diamonds (carat, cut, color, and clarity). Diamonds are the most valuable gemstone in the world.

Diamond Shapes
As the name suggests, shape (round, princess, radiant, etc.) describes a diamond’s form, primarily as viewed from above. All diamond shapes have different attributes, but overall the beauty of the individual shapes is a matter of personal taste.
Choose Your Diamond Shape
Since all diamond cut styles are very different, unique characteristics determine quality for each shape. Select your preferred shape below and learn how to recognize the most beautiful diamond in that shape.
ROUND



The round brilliant cut is the most popular diamond shape used in jewelry today. Diamond cutters have been using the physics of light behavior and mathematics to optimize fire (flashes of colored light reflected back from the diamond) and brilliance (light reflected up from the surface of the diamond) in a round diamond. To get a good balance of brilliance and fire of a round brilliant diamond select one of the two highest cut grades (Excellent or Very Good).
PRINCESS


This is the most popular non-round diamond. Its unique cut makes it popular in engagement rings. The princess cut has pointed corners and is traditionally square in shape. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in its corners.
EMERALD



The pavilion (bottom portion of the diamond) makes this shape different. It is cut with rectangular facets. It has a larger open table and hereby highlights the clarity of the diamond. To optimize appearance it is advisable to choose an emerald cut with a higher clarity grade (above SI). If you prefer an emerald cut with a squared outline, look at the Asscher cut diamond.
ASSCHER



This shape is very similar to the emerald cut, except that it is square. The Asscher cut also has a pavilion (bottom portion of the diamond) that is cut with rectangular facets in the same way as the emerald cut. To optimize appearance it is advisable to choose an emerald cut with a higher clarity grade such as VS. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in its corners.
MARQUISE



The shape of a marquise diamond allows cutters to maximize carat weight, giving a much larger-looking diamond. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in the points of the marquise. This style of cut looks beautiful set with round or pear-shaped side stones and the length of the marquise makes fingers appear long and slender.
OVAL



Oval diamonds have brilliance similar to a round diamonds. They are very popular as their length can accentuate long, slender fingers.
RADIANT


Trimmed corners are the unique feature of this style of cut. They help make the radiant cut versatile for use in jewelry. Radiant cuts look most stunning when set with either baguette or round side diamonds. Radiant cuts vary in their degree of rectangularity.
PEAR



This style of cut is also called a teardrop because of its single point and rounded end. The look of the pear shape makes it very popular in diamond jewelry. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in the point of the pear. If you choose an elongated pear shape, the length of the diamond can create a slimming illusion on the fingers.
HEART



The heart is a symbol of love and this makes it a popular choice for use in jewelry. When selecting a color grade, with lower color grades the color may be slightly visible in the point of the heart and corners.
CUSHION



Cushion cut diamonds are also known as pillow cut diamonds, they have rounded corners and larger facets. The larger facets highlight the diamond’s clarity and therefore to optimize appearance it is advisable to choose a cushion cut with a higher clarity grade (above SI).

The GIA’s mission is to increase consumers’ trust in diamonds and jewelry by upholding the highest standards of integrity, academics, science, and professionalism. They work toward this goal by providing jeweler and consumer education, conducting meticulous research, and developing state-of-the-art laboratory instruments for diamond inspections.
GIA Diamond Grading Standards
GIA diamonds are examined by a minimum of four highly trained diamond graders and gemologists. At each step of a diamond’s evaluation, a more senior staff member independently grades the stone. To ensure impartial evaluations, the distribution of diamonds to graders is a completely random process.
DIAMOND CARAT


Carat is the unique unit of weight measurement used to assess precious stones, including diamonds. Carat weight is sometimes misunderstood as a measure of physical size; nevertheless, it manifests in numerous ways depending on the shape and kind of stone being measured. The carat weight of a diamond is a major determinant in establishing its value and quality, among other criteria. The price of a diamond increases with its carat weight, while the other four Cs also have a role. Even while diamonds come in a wide range of carat weights, the most popular ones are between .25 and 5 carats. Schedule an appointment with one of our jewelers if you still have questions about diamond carat weight.
DIAMOND COLOR


Any diamond found in nature is almost certain to have some color to it. The price tag is directly proportional to the diamond’s quality. Although colorless diamonds do exist, they are quite uncommon. You should always anticipate that the diamond you buy will have some natural color to it. All sorts of stones with varying quantities of color are produced by chemical and physical methods. The absence of color in a diamond often results in a better-perceived quality.
DIAMOND CLARITY

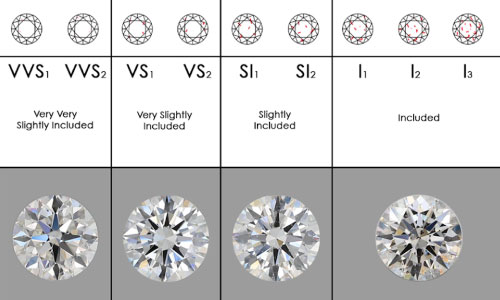
External flaws and interior flaws, known as blemishes and inclusions, respectively, are what give each diamond its unique appearance and quality. A diamond’s worth is directly proportional to the number and severity of its flaws. The lower the clarity grade, the more flaws there are in the diamond.
DIAMOND CUT GRADE

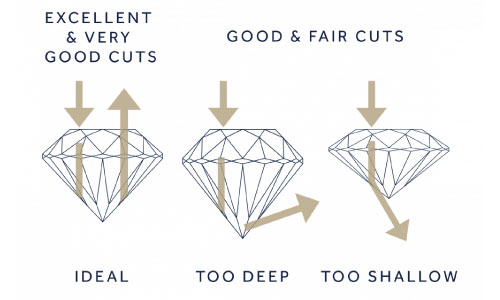
the cut grade is established for brilliant round-cut diamonds based on the analysis of the stone’s craftsmanship and light interaction. the level of a diamond’s craftsmanship is determined by evaluating its polish, symmetry, and proportions. the stone’s light interaction is based on its brightness, scintillation, and fire. the GIA designates the quality of a cut on a grading scale ranging from excellent to poor.
POLISH & SYMMETRY

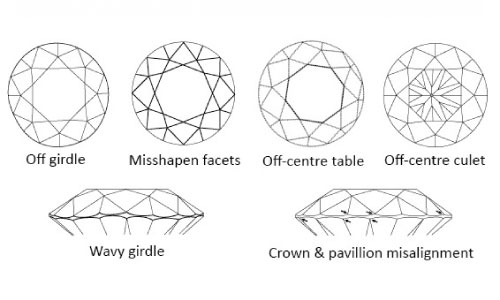
The polish and symmetry of a diamond are graded on a scale from good to poor. A thorough examination of the diamond’s workmanship is the basis for the final rating.
DIAMOND FLUORESCENCE


Based on how it reacts to ultraviolet light, a diamond is classified as having no fluorescence, a very weak fluorescence, a moderate amount of fluorescence, or a high fluorescence.
LASER INSCRIPTION


Diamonds may have their unique GIA report numbers laser engraved on the girdle for enhanced protection and identification. Every loose diamond that is graded by the GIA may also be laser inscribed with its unique grading number.
GIA Diamond Grading
The GIA Diamond Grading Report is issued for diamonds that fall in the D-Z color range. This detailed report a full quality analysis of shape and cutting style, measurements, carat weight, color grade, clarity grade, cut grade (for brilliant round-cut diamonds), polish and symmetry assessments, and fluorescence. The report also includes a plotted diagram indicating the relative size and location of clarity characteristics, a proportion diagram, and GIA grading scales.
Independent Diamond Certification
What is diamond certification, and how are diamonds independently certified? Independent certification is your assurance that you’re getting a quality diamond that is accurately graded without bias.
Before being purchased, many diamonds are sent to a third-party laboratory for comprehensive evaluation; this process is known in the industry as diamond certification. A respectable laboratory is one staffed by professional gemmologists who specialise in diamond grading. The diamond’s clarity, color, cut and weight is measured using a jeweler’s loupe, microscope, and other industry tools.
Laboratory certification provides an impartial judgement of the quality and characteristics of each diamond. The certificate (called a grading report or dossier) gives the purchaser added confidence that the diamond received is as described by the seller. The certificate is also valuable for insurance purposes, as it provides a professional and independent evaluation of the diamond.
It must be understood that a diamond certificate is not a valuation or appraisal. A valuation or appraisal will establish the value on an item (usually for insurance purposes). A diamond certificate does not assess the diamond’s market value, only its characteristics and quality. However, a diamond certificate from a reputable laboratory is very helpful to produce an accurate valuation or appraisal.

Choosing the Right Metal for Your Engagement/Bridal Ring
It’s time to buy an engagement/bridal ring — and there are so many factors to consider. Choosing the metal alone is a more complex decision than it used to be. Where it once was a simple choice between yellow and white, now you have a whole range of possibilities to consider, including:
- What’s the difference between white gold and platinum?
- What exactly is rose gold?
- How do newer, alternative metals popular in men’s wedding rings, like titanium and tungsten carbide, complement gold and platinum in engagement/bridal rings?
Take it one step at a time — starting with the type of metal — and you’ll end up with a ring that suits her style and that she’ll cherish forever. Use this as your guide to the different types of metals available for ring settings.
YELLOW GOLD


Yellow gold is a timeless metal that has recently been back in style. Its classic patina is achieved by combining the red of copper and the green of silver. When compared to white gold, yellow gold fell out of favor for a time but has now made a comeback.
WHITE GOLD


White gold, which is more modern than yellow gold, is made by alloying yellow gold with copper, zinc, and nickel, which gives it a silvery white color (or palladium). Rhodium, a member of the platinum group metals, is used to plate white gold, making it more durable, resistant to scratches and tarnishing, and, of course, white. Over time, though, the plating might wear off and need to be reapplied at the jeweler.
ROSE GOLD


Rose gold’s unique and enticing pink color comes from the addition of a copper alloy to traditional yellow gold. Rose gold, like yellow and white gold, is made from a variety of metal alloys, but the specific proportions of those alloys give the metal its distinctive pink hue.
Platinum

Diamonds are elegantly highlighted by platinum, a naturally white metal with a cool shine. It is the most valuable of jewelry metals, hence it is often used for engagement and wedding rings.
Platinum, when used as jewelry, is five times rarer than gold and five times purer. Platinum is strong and long-lasting, making it a great choice if your fiancée is always on the run; its density makes it an ideal material for placing precious stones like diamonds or jewels. Platinum is wonderful for persons with sensitive skin since it is hypoallergenic by nature.
Metal Karat

Troy ounces are the standard weight measurement when working with gold. Specifically, 20 pennyweights in troy are equal to 1 ounce in troy. The pennyweight (dwt.), equal to 1.555 grams, is a typical unit of measure in the jewelry trade.
Sizes of Common Bars
- In terms of troy ounces, that’s 400. (12.5 kilos)
- The weight is 32.15 troy ounces (1 kilo)
- One hundred and eighty ounces of troy weight (3.11 kilos)
Tips for Prong Options
The biggest tip for buyers considering different prong options is to think about their everyday lifestyle. It is much more important to find a ring that is added seamlessly than a ring that is beautiful but requires special treatment. Whether the buyers choose a claw prong engagement/bridal ring, a heart prong engagement/bridal ring, a high prong engagement/bridal ring, or a shared prong engagement/bridal ring, they still have to consider the choice of metal and the number of prongs in order to find a ring that is perfect for them.


 JAN | Garnet
JAN | Garnet FEB | Amethyst
FEB | Amethyst MAR | Aquamarine
MAR | Aquamarine APR | Diamond
APR | Diamond MAY | Emerald
MAY | Emerald JUN | Pearl & Alexandrite
JUN | Pearl & Alexandrite JUL | Ruby
JUL | Ruby AUG | Peridot
AUG | Peridot SEP | Sapphire
SEP | Sapphire OCT | Opal & Pink Tourmaline
OCT | Opal & Pink Tourmaline NOV | Citrine
NOV | Citrine DEC | Blue Topaz & Tanzanite
DEC | Blue Topaz & Tanzanite JAN | Garnet
JAN | Garnet FEB | Amethyst
FEB | Amethyst MAR | Aquamarine
MAR | Aquamarine APR | Diamond
APR | Diamond MAY | Emerald
MAY | Emerald JUN | Pearl & Alexandrite
JUN | Pearl & Alexandrite JUL | Ruby
JUL | Ruby AUG | Peridot
AUG | Peridot SEP | Sapphire
SEP | Sapphire OCT | Opal & Pink Tourmaline
OCT | Opal & Pink Tourmaline NOV | Citrine
NOV | Citrine DEC | Blue Topaz & Tanzanite
DEC | Blue Topaz & Tanzanite